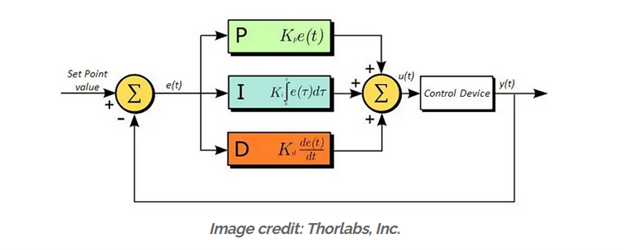
For my discussion, I choose to talk about how derivatives are used for servo motor controls. First, we need to discuss what a servo motor is and what it does. A servo motor is a current and voltage-controlled electrical motor. This motor works on a closed-loop system through the commands of a servo controller which uses a feedback device to control the velocity and position of the servo. A great example of this would be the cruise control in a car. The servo controller would be the driver setting cruise control to a set speed which sends a voltage signal and varying current to the servo which controls the throttle until you get to a certain speed, then maintains that speed. The feedback device would be your tachometer telling the servo to lower the current being sent if you go over the set speed and to raise the current if you go under the set speed. The servo is using Proportional Integral Derivative or PID which changes the motor’s output based on the set speed and what the tachometer reads. The PID algorithm uses Proportional feedback which tells the servo that it needs to go faster to reach the set speed increasing current sent to the servo. Derivative feedback tells the servo that we are over the set speed, and it doesn’t need to run anymore decreasing current sent to the servo. Integral feedback holds the current at its set amps and holds the position of the servo to keep the set speed without any outside interactions that would call for the need of the other two. Below is an image of how the PID algorithm works.
(Collins, 2022)
When put into an equation it will look something like this:
Apmonitor.com (n.d.)
Thank you for reading.
References:
Collins, D. (2022, October 17). FAQ: What are servo feedback gains, overshoot limits, and position error limits? Motion Control Tips. https://www.motioncontroltips.com/faq-what-are-servo-feedback-gains-overshoot-limits-position-error-limits/Links to an external site.
Proportional Integral Derivative (PID). (n.d.). https://apmonitor.com/pdc/index.php/Main/ProportionalIntegralDerivativeLinks to an external site.